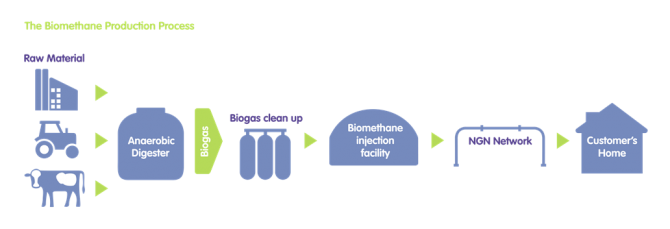
From Waste to Warmth
Biomethane is produced from organic material such as green waste; food industry waste; agricultural waste and industrial waste.
In a biological process known as anaerobic digestion, microorganisms break down the material in the absence of oxygen. One of the end products is biogas.
This gas can be combusted to generate electricity and heat, or can be cleaned to remove impurities and upgraded to biomethane, to be injected into the gas distribution network.
Injecting biomethane into the grid is far more energy efficient than using the gas to generate electricity. Around 90% energy is retained through grid injection, but just 30-35% when combusted to generate electricity. Combustion also leads to the escape of methane into the air, which contributes to the build-up of harmful greenhouse gasses.